The PDXpower package can conduct power analysis for
time-to-event outcome based on empirical simulations.
You can install the development version of PDXpower from
GitHub with:
# install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_github("shanpengli/PDXpower")Below is a toy example how to conduct power analysis based on a
preliminary dataset animals1. Particularly, we need to
specify a formula that fits a ANOVA mixed effects model with correlating
variables in animals1, where ID is the PDX
line number, Y is the event time variable, and
Tx is the treatment variable.
Next, run power analysis by fitting a ANOVA mixed effects model on
animals1.
library(PDXpower)
data(animals1)
### Power analysis on a preliminary dataset by assuming the time to event is log-normal
PowTab <- PowANOVADat(data = animals1, formula = log(Y) ~ Tx,
random = ~ 1|ID, n = c(3, 5, 10), m = c(2, 3, 4), sim = 100)
#> Parameter estimates based on the pilot data:
#> Treatment effect (beta): 0.7299
#> Variance of random effect (tau2): 0.0332
#> Random error variance (sigma2): 0.386
#>
#> Monte Carlo power estimate, calculated as the
#> proportion of instances where the null hypothesis
#> H_0: beta = 0 is rejected (n = number of PDX lines,
#> m = number of animals per arm per PDX line,
#> N = total number of animals for a given combination of n and m):
#> n m N Power (%)
#> 1 3 2 12 43
#> 2 3 3 18 65
#> 3 3 4 24 77
#> 4 5 2 20 70
#> 5 5 3 30 87
#> 6 5 4 40 95
#> 7 10 2 40 98
#> 8 10 3 60 99
#> 9 10 4 80 100The following code generates a power curve based on the object
PowTab.
plotpower(PowTab[[4]], ylim = c(0, 1)) Alternatively, we may also conduct power analysis based on median
survival of two randomized arms without the preliminary data. We suppose
that the median survival of the control and treatment arm is 2.4 and
7.2, assuming the intra-class correlation of 10%, a power analysis may
be done as below:
Alternatively, we may also conduct power analysis based on median
survival of two randomized arms without the preliminary data. We suppose
that the median survival of the control and treatment arm is 2.4 and
7.2, assuming the intra-class correlation of 10%, a power analysis may
be done as below:
### Assume the time to event outcome is log-normal distributed
PowTab <- PowANOVA(ctl.med.surv = 2.4,
tx.med.surv = 7.2, icc = 0.1, sigma2 = 1, sim = 100,
n = c(3, 5, 10), m = c(2, 3, 4))
#> Treatment effect (beta): -1.098612
#> Variance of random effect (tau2): 0.1111111
#> Intra-PDX correlation coefficient (icc): 0.1
#> Random error variance (sigma2): 1
#>
#> Monte Carlo power estimate, calculated as the
#> proportion of instances where the null hypothesis
#> H_0: beta = 0 is rejected (n = number of PDX lines,
#> m = number of animals per arm per PDX line,
#> N = total number of animals for a given combination
#> of n and m):
#> n m N Power (%)
#> 1 3 2 12 37
#> 2 3 3 18 56
#> 3 3 4 24 85
#> 4 5 2 20 65
#> 5 5 3 30 80
#> 6 5 4 40 97
#> 7 10 2 40 93
#> 8 10 3 60 99
#> 9 10 4 80 100
plotpower(PowTab, ylim = c(0, 1))
Alternatively, one can run power analysis by fitting a Cox frailty
model. Here we present another dataset animals2.
Particularly, we need to specify a formula that fits a Cox frailty model
with correlating variables in animals2, where
ID is the PDX line number, Y is the event time
variable, Tx is the treatment variable, and
status is the event status.
data(animals2)
### Power analysis on a preliminary dataset by assuming the time to event is Weibull-distributed
PowTab <- PowFrailtyDat(data = animals2, formula = Surv(Y, status) ~ Tx + cluster(ID),
n = c(3, 5, 10), m = c(2, 3, 4), sim = 100)
#> Parameter estimates based on the pilot data:
#> Scale parameter (lambda): 0.0154
#> Shape parameter (nu): 2.1722
#> Treatment effect (beta): -0.8794
#> Variance of random effect (tau2): 0.0422
#>
#> Monte Carlo power estimate, calculated as the
#> proportion of instances where the null hypothesis
#> H_0: beta = 0 is rejected (n = number of PDX lines,
#> m = number of animals per arm per PDX line,
#> N = total number of animals for a given combination
#> of n and m,
#> Censoring Rate = average censoring rate across 500
#> Monte Carlo samples):
#> n m N Power (%) for Cox's frailty Censoring Rate
#> 1 3 2 12 36.49 NA
#> 2 3 3 18 42.35 NA
#> 3 3 4 24 62.22 NA
#> 4 5 2 20 49.30 NA
#> 5 5 3 30 69.23 NA
#> 6 5 4 40 78.72 NA
#> 7 10 2 40 90.57 NA
#> 8 10 3 60 88.78 NA
#> 9 10 4 80 96.91 NA
plotpower(PowTab[[5]], ylim = c(0, 1))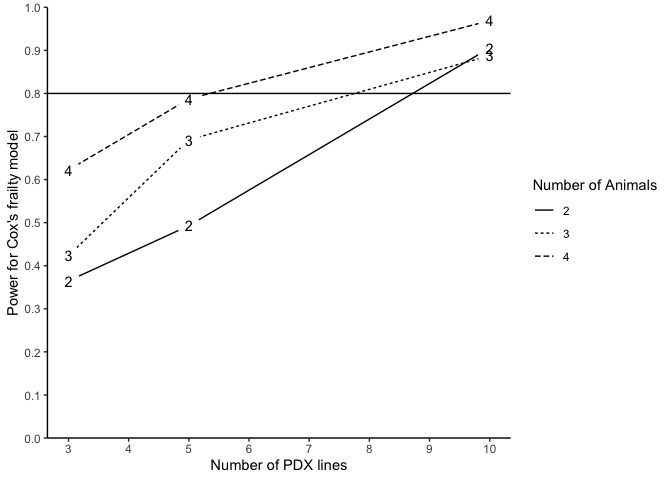
Alternatively, we may also conduct power analysis based on median
survival of two randomized arms. We suppose that the median survival of
the control and treatment arm is 2.4 and 4.8, allowing a PDX line has
10% marginal error (tau2=0.1) of treatment effect and an
exponential event time, a power analysis may be done as below:
### Assume the time to event outcome is weibull-distributed
PowTab <- PowFrailty(ctl.med.surv = 2.4, tx.med.surv = 4.8, nu = 1, tau2 = 0.1, sim = 100,
n = c(3, 5, 10), m = c(2, 3, 4))
#> Treatment effect (beta): -0.6931472
#> Scale parameter (lambda): 0.2888113
#> Shape parameter (nu): 1
#> Variance of random effect (tau2): 0.1
#>
#> Monte Carlo power estimate, calculated as the
#> proportion of instances where the null hypothesis
#> H_0: beta = 0 is rejected (n = number of PDX lines,
#> m = number of animals per arm per PDX line,
#> N = total number of animals for a given combination
#> of n and m,
#> Censoring Rate = average censoring rate across 500
#> Monte Carlo samples):
#> n m N Power (%) for Cox's frailty Censoring Rate
#> 1 3 2 12 22.45 NA
#> 2 3 3 18 21.05 NA
#> 3 3 4 24 41.41 NA
#> 4 5 2 20 35.16 NA
#> 5 5 3 30 44.79 NA
#> 6 5 4 40 62.89 NA
#> 7 10 2 40 67.01 NA
#> 8 10 3 60 73.74 NA
#> 9 10 4 80 86.73 NA
plotpower(PowTab, ylim = c(0, 1))